Opinion: Australia is in a unique position to eliminate the bee-killing Varroa mite. Here’s what happens if we don’t
by Scarlett Howard, Alexander Mikheyev, Emily Remnant, Simon Tierney and Théotime Colin, The Conversation

Credit: Théotime Colin, Author provided Varroa mites—notorious honey bee parasites—have recently reached Australian shores, detected at the Port of Newcastle in New South Wales last year. If they establish here, there would be significant implications for agricultural food security, as honey bees are heavily relied on for the pollination of many crops.
However, while Australia is the last continent to be invaded by the mite, it has an opportunity to be the first to eradicate it.
Varroa destructor is a small mite that attaches to bees and eats their “fat body.” The fat bodies of honey bees are the insect equivalent of a liver. Varroa weakens bees, reduces their lifespan and increases the spread of deadly viruses.
Scientists need to be ready: this might be Australia’s best chance to collect important data on the spread and evolution of this parasite. Our new paper published today in Biology Letters outlines what questions scientists need to ask and what data they need to collect if Varroa spreads in Australia.
Such data could help us understand how parasites evolve, why Varroa are so damaging for honey bees, and how Varroa mites impact other insects and the environment.
Will Varroa establish in Australia?
Australia is in close proximity to countries that have the mite, including New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, Timor-Leste and Indonesia.
This probably explains why invasive honey bee swarms are frequently intercepted at our ports, many of these carrying Varroa. Australia currently bans importation of honey bee colonies due to the biosecurity risk, so these interceptions are typically due to stowaway swarms taking up residence in shipping containers.
Previous invasions of Varroa have been successfully eradicated before establishing, but this time Varroa circumvented the biosecurity surveillance near Newcastle and spread locally.
The New South Wales Department of Primary Industries has been contact-tracing and culling hives in contaminated areas, and the spread has been slow so far. Australia has large populations of feral honey bees, which could potentially act as a reservoir for Varroa and are much harder to trace and control, so the department is tackling this with a wild honey bee baiting program.
What threats does Varroa pose?
Varroa mites are a threat to food security. Although Australia has an abundance of food and exports it to other nations, the price of food is likely to increase if Varroa escapes confinement.
Currently, pollination of crops in eradication zones such as berries in Coffs Harbor is at risk due to the removal of all honey bees in the region, which may lead to short-term increases in food costs.
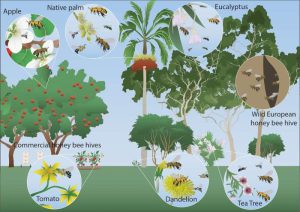
Australia currently relies on pollination by commercial honey bees (yellow), supplemented by feral honey bees (brown), though we have many native bee species like stingless bees and blue banded bees that are also being used in crop pollination. Credit: Boris Yagound, adapted from Chapman et al. 2023, CC BY
However, establishment and spread of Varroa will lead to lower pollination and lower crop production across the country, which will raise the price of most fruit and vegetables that depend on bee pollination.
This could worsen the food affordability crises caused by the current inflation, affecting the ability of low income households to buy nutritious and fresh produce. Almond pollination has already noted a deficit of 80,000 hives in the last season.
Many of the honey bee colonies that pollinate our crops are thought to be feral, living in tree hollows or nest-boxes designed for native animals. These feral bees are not managed by beekeepers and so won’t be saved by the use of Varroa treatments, meaning they will most likely disappear.
To read the complete article go to; Opinion: Australia is in a unique position to eliminate the bee-killing Varroa mite. Here’s what happens if we don’t (phys.org)
We are here to share current happenings in the bee industry. Bee Culture gathers and shares articles published by outside sources. For more information about this specific article, please visit the original publish source: Opinion: Australia is in a unique position to eliminate the bee-killing Varroa mite. Here’s what happens if we don’t (phys.org)








